Vitamin D may be available if you get enough exposure to radiation from the sun and your body is able to take full advantage, but more than 1 in 3 people may have low levels. That is a problem because vitamin D is necessary for building and maintaining strong bones, as well as lowering risk for conditions such as autoimmune conditions, certain types of cancer, and heart disease.
Exposing yourself to sunlight, eating foods that are naturally high in vitamin D or that are fortified with it, and taking supplements such as a Vitamin D3 Patch with Calcium or a Vitamin D3 Patch with Vitamin K2, are some effective ways to get vitamin D.
From Sunlight
When UV radiation from the sun hits the skin, a process that includes the liver and kidneys can lead to the formation of vitamin D3 in the body. Vitamin D3 is the active form of vitamin D. However, this process breaks down if you do not get enough radiation or if for various reasons your liver and kidney do not kick in.
From Food
VItamin D is naturally found in fatty fish and eggs. It can also be in fortified foods such as milk, as well as some milk substitutes, yogurt, cereal, and orange juice. The problem is that only a limited number of foods contain vitamin D naturally or as the result of fortification. If you do not tend to eat these foods, you may not get enough vitamin D.
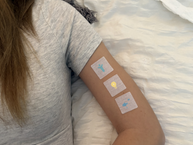
From a Vitamin Patch
Taking vitamin D3 capsules or other oral supplements can increase vitamin D levels, but certain PatchAid Patches also contain high levels of vitamin D3.
With vitamin patches, there is no need to swallow pills or worry about effects such as stomach discomfort. Instead, you can stick the patch onto a patch of clean skin and leave it on for up to 8 hours as the transdermal delivery system kicks in.
What to Do If You May Have a Vitamin D Deficiency
It is important to talk to your doctor if you have a vitamin D deficiency. It is also important to talk to your doctor to find out whether you have a vitamin D deficiency if you have risk factors for one. People at higher risk for vitamin D deficiency include the following.
- Older adults.
- People who are following a vegan, lactose-free, or paleo diet.
- Bariatric surgery patients.
- People on strict or restrictive diets, including very low-calorie diets and fad diets.
- People who live in northern climates where sunlight and UV radiation are limited during winter months.
- People with darker skin.
- People who wear sunscreen every time they go outside.
- People who are overweight or obese.
- People with liver or kidney disease.
A simple blood test can determine your vitamin D levels. If you have suboptimal levels, you and your doctor can determine whether you need a vitamin D supplement and which may be best for you.
When choosing how to increase vitamin D levels, you will want to consider factors such as the easiest ways to get vitamin D. A Vitamin Patch from PatchAid may be the answer if you are looking for high levels and convenience.