Do you need a vitamin C supplement? Getting enough vitamin C is known to support your body in fighting infections. But vitamin C’s role in immunity may also be related to your seasonal allergy symptoms. The Vitamin C Plus Patch from PatchAid is specifically designed to have higher amounts of vitamin C than you are getting from your diet, and it has other ingredients to support antioxidant benefits.*
Here’s what you should know about taking vitamin C for allergies. Be sure to discuss any allergies with your healthcare provider, and ask before taking any dietary or nutritional supplements.
Vitamin C and Your Body
Vitamin C has many roles in the body. It’s needed to produce strong collagen, which helps with firm skin and healthy joints. It helps your body absorb iron, so you can produce healthy red blood cells and prevent iron-deficiency anemia. It is needed to keep your immune system strong. And it is an antioxidant.
Sufficient vitamin C can help:*
- Promote a healthy heart.
- Maintain normal blood pressure.
- Support brain health.
- Maintain eye health during aging.
- Prevent cellular damage due to oxidation.
So what do these have to do with allergies? Let’s take a look.
Allergies and Your Immune System
First, let’s make the connection between allergies and the immune system. Allergic reactions are the result of your body’s immune system responding to something that is external to it. Food allergies are a response to a protein in food, such as to a protein in peanuts, soy, or milk. Other allergies can be the result of a response to dust, pollen, pet fur, or hay. You might notice seasonal allergies, which means your body is mounting a response to something that is in the air only during some times of the year.
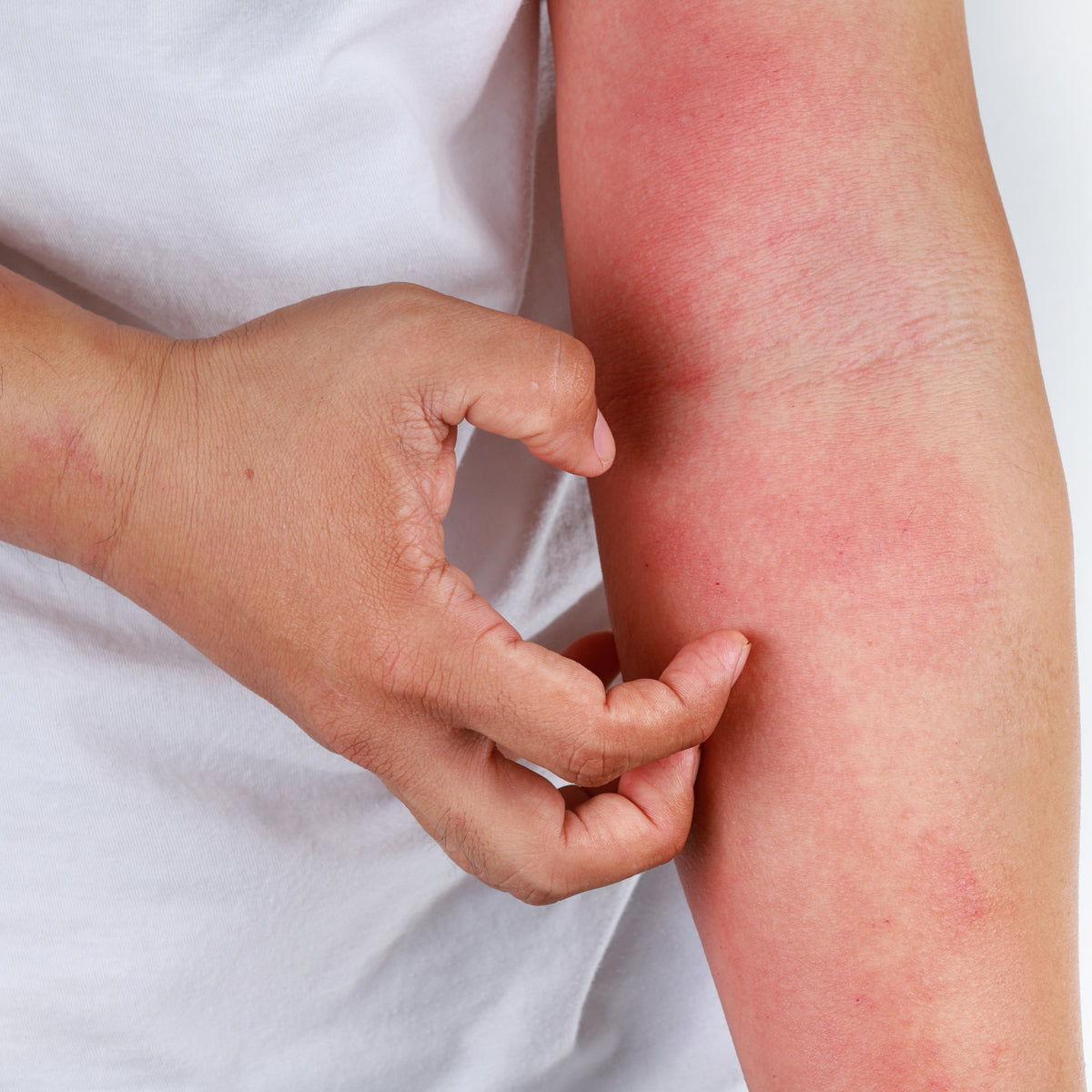
Symptoms of allergies are caused by compounds called histamines that your body produces. These are common symptoms.
- Runny nose
- Sneezing
- Itchy skin
- Red or watery eyes
- Rash
More severe allergies can lead to asthma or anaphylaxis. Be sure to contact your healthcare provider immediately if you get such symptoms or are unsure.
Histamines and Vitamin C
Now, where does vitamin C come in? Vitamin C isn’t just needed for a strong immune system, healthy joints, and antioxidant activity, but it is also an antihistamine. Does that make you wonder if it can fight histamines that cause symptoms of allergies?
If you have allergies, you might first ask your doctor about antihistamine medications. These drugs work by blocking receptors for histamines. That means histamines won’t be able to cause symptoms that you associate with allergies.
The way vitamin C works as an antihistamine is a little bit different from the way antihistamine medication works. Vitamin C works by targeting production of antihistamines. Your body can produce fewer antihistamines, which would theoretically lead to fewer symptoms of allergies.
Natural Food Sources of Vitamin C
There are good food sources of vitamin C. Certain fruits and vegetables are the best natural sources of vitamin C. The following are examples of good sources.
- Bell peppers
- Tomatoes
- Onions
- Broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage
- Spinach and kale
- Potatoes
- Citrus fruit, such as oranges, limes, lemons, tangerines, and grapefruits
- Kiwi fruit
- Cantaloupe
- Mangos
- Strawberries and other berries
Still, a vitamin C supplement can give you more vitamin C than you can probably get from your diet on a regular basis.
Vitamin C Supplements
There are many forms of vitamin C supplements. You can get vitamin C from capsules, liquids, and chewable tablets, for example. Vitamin C is a water soluble vitamin, and it is likely safe in high doses. There are some concerns about diarrhea in very high doses. With a vitamin C patch, there’s no need to worry about digestion and absorption of the nutrients.
Vitamin C Plus Patch by PatchAid
The Vitamin C Plus Patch by PatchAid lets you avoid any oral supplements while you get a whopping dose of vitamin C. To give you an idea of how much vitamin C, consider this: while an orange has 65 mg of vitamin C, the Vitamin C Plus Patch has 2,500 mg. The vitamin C in this patch is from acerola cherries.
It also has various antioxidants, such as from citrus bioflavonoids and rutin, which is naturally found in buckwheat, asparagus, and raspberries. Barley powder and alfalfa powder may support heart health and a normal metabolism,* and this patch also has rosehip, which is one of the most concentrated natural sources of vitamin C.
Vitamin Patches are easy to use. Just peel off the backing and stick the patch onto a smooth, clean, and dry area of skin. Leave the patch on for up to 8 hours. Then remove the patch and discard it. Repeat with a new patch the next day. As long as your doctor agrees, it’s fine to use multiple PatchAid Patches at one time.
Vitamin D for Allergy Support
If you’re looking to fully support your immune system, you might want to also consider using a Vitamin D3 Patch by PatchAid. Vitamin D is needed for a strong immune response and to reduce autoimmune responses, but it is low in a good portion of the population. Vitamin D3 Patches by PatchAid come with supporting nutrients, such as calcium, vitamin K, and magnesium, to keep bone health in mind as well.
Allergies and their symptoms are no fun, so it makes sense to look for ways to calm your immune system if you are experiencing allergies. Vitamin C and vitamin D are both related to the immune response. The Vitamin C Plus Patch and Vitamin D3 Patches by PatchAid are both rich in these and related nutrients, and they’re easy and convenient to use. Be sure to talk to your healthcare provider about any allergies you have and before using a nutritional supplement.
*The Food and Drug Administration has not evaluated these statements. PatchAid patches are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease. Anyone with a medical condition should seek the advice of a licensed medical practitioner. Individual results may vary.