Vitamin K does not always get as much attention as some other vitamins and minerals, but it is just as essential to life and optimal health. Deficiency can lead to excessive bleeding. If you need additional vitamin K, the PatchAid Vitamin D3 Patch with K2 is an easy-to-use supplement.* Ask your healthcare provider if you may be low in vitamin K and whether the patch may be right for you.
What Is Vitamin K?
Vitamin K is one of the fat-soluble vitamins, along with vitamins A, D, and E. It is named for its role in blood clotting; the “K” in vitamin K comes from the German word, “koagulation,” for coagulation. Vitamin K can be in the form of K1, or phylloquinone, K2, or menaquinone, or K3, or menadione.
Even though it’s fat-soluble, your body does not store much vitamin K. Instead, it helps maintain enough in the body by recycling it.
Vitamin K and Blood Clotting
Vitamin K may be best known for its role in blood clotting. Too much blood clotting is bad, such as clots that cause a stroke or heart attack, but blood clotting is essential for life. Think about it like this. When you bruise or cut yourself, you eventually stop bleeding naturally. That’s because your blood clots itself. Vitamin K has essential roles in the reactions that lead to blood clotting.
Vitamin K and Bones
Vitamin K is also essential for healthy bones. Specifically, vitamin K is a necessary part of reactions that create proteins such as osteocalcin. Osteocalcin allows your body to create and deposit bone mineral, which includes minerals such as calcium and magnesium.
Sources of Vitamin K
Vitamins K1 and K2 are found naturally in some food sources. Vitamin K3 is synthetic and only available in some supplements. These are some food sources of vitamin K.
- Mustard and collard greens
- Broccoli and spinach
- Berries and canned pumpkin
- Olive and canola oil
- Hard cheese, such as cheddar and swiss
- Butter and yogurt
- Eggs and egg yolks
- Beef, pork, and chicken
- Fermented foods, such as kimchi, natto, and sauerkraut.
Signs of Deficiency and Risk Factors
You may not know you are low in vitamin K, but you may have some symptoms. A clue may be if you notice excessive bleeding when you hurt yourself. Instead of having just a minor cut or bruise, it may be bigger than you expect. It is also possible to have very heavy menstrual cycles or to see blood in your stools due to excessive bleeding.
You may be at higher risk for vitamin K deficiency if you have a fat malabsorption disorder, since vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin. Bariatric surgery patients can be at risk for vitamin K deficiency, as can people with IBD or celiac disease. In addition, taking high amounts of vitamin A or vitamin E as supplements can impair vitamin K status. Finally, a variety of medications interact with vitamin K, and can alter your vitamin K levels.
Testing Vitamin K Levels
Do you need vitamin K? How would you know? It is rare for a person to get a direct assessment of vitamin K levels. Instead, if your provider thinks that you may be low in vitamin K, you may get a test for clotting. The lab will draw your blood and measure how long your blood takes to clot. Taking longer than normal may be a sign that your vitamin K levels are low.
Topical Patch for Vitamin K
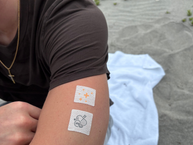
The Vitamin D3 with K2 Vitamin Patch is a vitamin K supplement that is an alternative to taking oral pills. Instead of needing to swallow capsules or liquids, or chew tablets, you can stick a patch onto your skin. The nutrients are absorbed transdermally without any need to go through the digestive process.
The Vitamin D3 with K2 Vitamin Patch has vitamin K in the form of K2, or menaquinone, which has not been found to be risky at high levels.* The patch has 290 mcg of K2. It also has the following nutrients.
- 5300 IU of vitamin D in the form of D3, which is the active form
- 300 mg of magnesium
- 105 mg of calcium
Vitamin D3, calcium, and magnesium are all important in bone health, just like vitamin K. Calcium and magnesium are minerals in bone, and vitamin D3 allows your body to use them properly. These nutrients are also important in immune function, heart health, and nerve and muscle function.*
The Vitamin D3 with K2 Vitamin Patch:
- May support strong bones.*
- May support heart, brain, breast, and colon health.*
- May promote healthy insulin-producing pancreatic cells.*
- May support healthy energy regulation.*
- May promote immune system function.
It is easy to use PatchAid Patches. Clean and dry an area of skin that is smooth and preferably hairless. Apply the patch after removing the backing. Leave it on for up to 8 hours while you sleep or go about your usual daily routine. The patch is okay while showering or exercising, too. After 8 hours, remove the patch and discard it. Repeat with a new patch the next day.
The Vitamin D3 with K2 Vitamin Patch is available in a 30-day or 3-month, 6-month, or 12-month supply. PatchAid patches are designed to be safe when using up to 8 patches at once. Just ask your healthcare provider about the best choices for you.
Insufficient vitamin K can put your bones at risk, and lead to bleeding and risk for cardiovascular conditions. The PatchAid Vitamin D3 Patch with K2 is easy to use and high in this vitamin, along with vitamin D and calcium. Ask your healthcare provider if it may be right for you, and always contact your healthcare provider about any health concerns and before taking any nutritional supplements.
*The Food and Drug Administration has not evaluated these statements. PatchAid products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease. Anyone with a medical condition should seek the advice of a licensed medical practitioner. Individual results may vary.